
/pencil-sketch-a-nude-female-body.jpg)
The pelvic region is represented from the front and from behind by a more flattened trapezium, whose base is as wide as the shoulders.įrom the side and when foreshortened it assumes the schematic appearance of a cuneiform box to contain the buttocks. The thoracic region can be represented from the front and from behind by a trapezium (1-4-5) whilst from the side and when foreshortened it assumes a more rounded aspect, almost like a barrel. The basic form of the torso is made up of two moving structures, the thoracic region and the pelvic region. In profile we can see at the front the shape of the thoracic region and at the rear the shape of the pelvic region, The lower part of the upper body is formed by the pelvic wedge, which extends backwards to the sacrum and the buttocks, whose medium-sized and large muscles have the shape of a butterfly. The main features of the back are the shoulder-blades, which follow the movement of the arms, and the spinal column, which elevates the upper body and allows by means of its particular anatomical structure an infinite number of positions and movements.
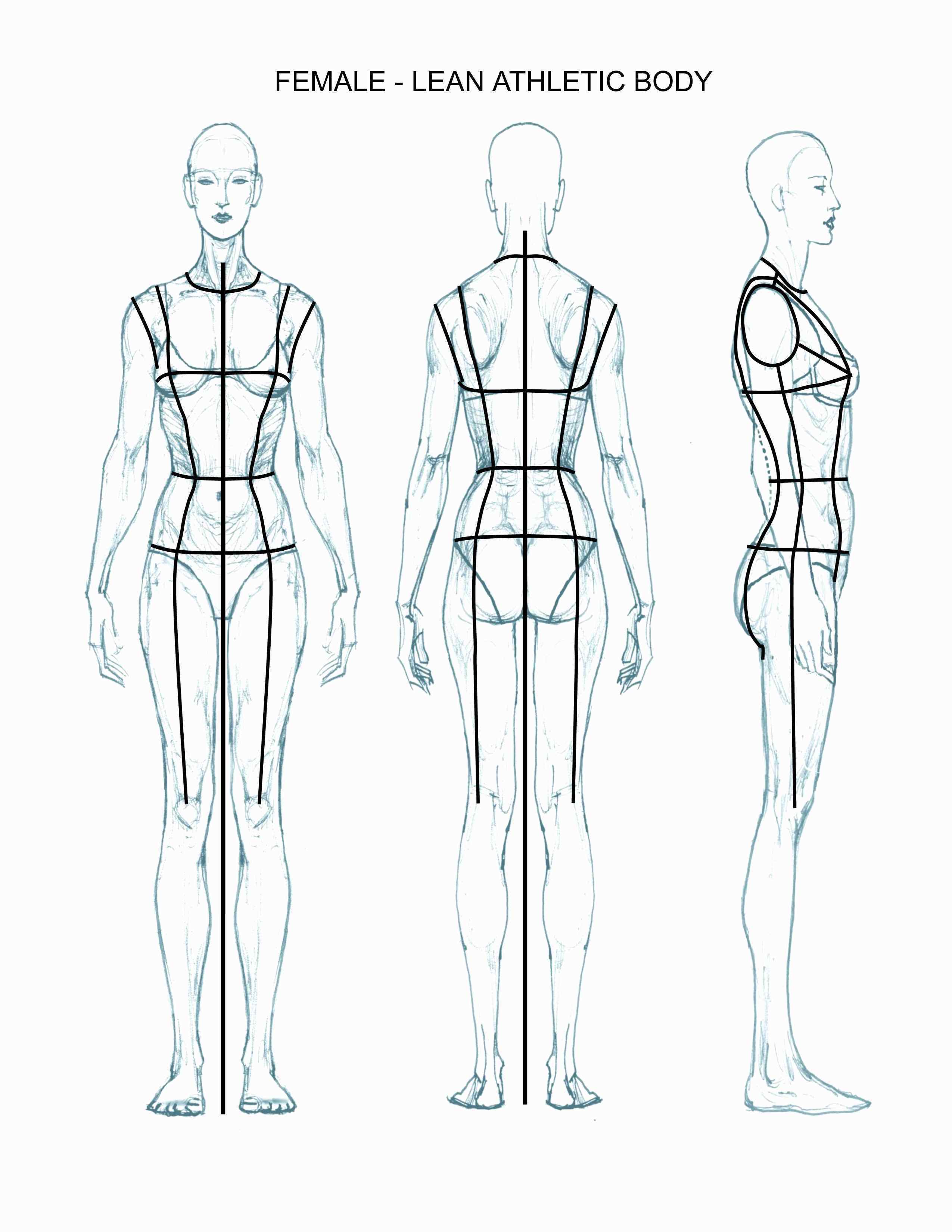
The pelvic region is formed by the stomach with the navel, by the hips and the pubic region. The upper body joins the hips at the waist, which is much smaller and slightly elevated in contrast to a man's. The shape of the breasts in an adolescent girl resembles an upside-down goblet and the dimensions can vary according to the type of build. To find the exact position of the nipples it is useful to draw two lines at 45° from the hollow of the neck through the ribcage, it will be noted by so doing that the nipples are orientated towards the outside. Then we have the thorax, which is the single largest structure in the body, formed by the ribs, the sternum, the protruding breasts and the armpits.

These anatomical features also constitute the main difference between the female body, which is rounder and more flexible, and the male body which is more imposing and muscular.Ī frontal view reveals the following features from top to bottom: the neck, cylindrical in form and nestling in the upper body behind the collarbone, the shoulders which are smaller than those of the male and of the same width as the hips, the collarbones, bones in the shoulders that join up as they dip in the cavity of the neck. Structurally it is made up of two moving parts of different sizes, the thoracic region and the pelvic region. Proportionately speaking, the upper body extends over two and a half units of measure of the overall female figure. Carrying out numerous exercises is therefore indispensable to achieve the necessary harmony for each pose. By contrast, an upper body in which the proportions are badly rendered or which is drawn too rigidly undermines the entire figure and throws its wearability off balance, rendering the fashion plate listless and impractical, in order to move so expressively, models practise at length the art of walking with an air of dignity, and to understand realistically every slightest rotation, every tension and every muscular coordination, much attention must be lavished even on the smallest movement.
#Female body sketch how to
The upper body is the key to the fashion plate and knowing how to reproduce it perfectly from every angle and in its every movement is a sign of great artistic ability. Stylists like to place it in evening dress with a surprising decolletage or to emphasize its curvaceousness in highly feminine suits. The upper body, or torso, is certainly the most important anatomical part of the female figure its extreme plasticity and shape make it an important protagonist in so many ways.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
